Melasma
Melasma
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a common, chronic skin condition characterized by the development of symmetrical, dark patches on the face and, less frequently, other parts of the body. Although melasma is not harmful, it can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life due to its cosmetic appearance. 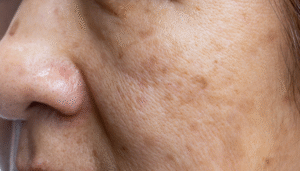
Whom does Melasma affect?
Melasma predominantly affects:
- Women, particularly those with darker skin tones
- After the age of 35 years of age.
- Men can also develop melasma, though it accounts for only a small percentage of cases.
- Geographically, melasma is more prevalent in regions with high ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure.
Etiology and Risk Factors
The exact cause of melasma remains unclear, but several contributing factors have been identified:
- Hormonal Influence: Pregnancy, oral contraceptives, and hormone replacement therapy are significant triggers due to fluctuations in oestrogen and progesterone levels.
- Ultraviolet Radiation: The sun exposure leading to melasma is not acute but rather cumulative over time. For example, consider 10–20 minutes of sun exposure every day over a period of 30–40 years. This cumulative damage manifests as melasma later in life. Although it may appear to develop suddenly, it is actually the result of prolonged exposure.
- Genetic Predisposition
- Medications and Cosmetics: Certain medications and skincare products can sensitize the skin to sunlight, aggravating melasma.
How is Melasma Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on history and physical examination. A Wood’s lamp can be used to determine the depth of pigmentation. In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions that closely mimic melasma.
Management and Treatment
Effective management of melasma requires a multifaceted approach:
- Sun Protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) and protective clothing.
- Topical Therapies:
- Hydroquinone: A gold-standard depigmenting agent that inhibits melanin synthesis. But it is a double-edged weapon in darker skin types and therefore needs meticulous supervision by a dermatologist.
- Other agents: Azelaic acid, kojic acid, retinoids, tranexamic acid etc,.
- Procedural Treatments:
- Chemical peels
- Microneedling
- Mesotherapy involving infusion of agents like tranexamic acid, glutathione etc.,
- Laser and light-based therapies (e.g., fractional lasers, Q switched lasers)
- Oral Medications: Emerging treatments, such as tranexamic acid, glutathione show better response when combined with in- clinic procedures.
As mixed melasma is the commonest type, combination of treatments to target both the superficial and deeper pigmentation is often essential.
Melasma is a challenging yet manageable skin condition that requires patience and collaboration from both the doctor and the patient.
Melasma Treatment at Reflect Skin & Hair Clinic, Coimbatore is done in a systematic way tailored to the patient’s needs. It involves a combination of preventive measures, patient education, and treatment methods tailored to the patient’s needs, considering both practicality and economic feasibility.
