Urticaria
Urticaria (Hives)
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, itchy wheals that appear suddenly. Urticaria can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (persisting for more than six weeks).
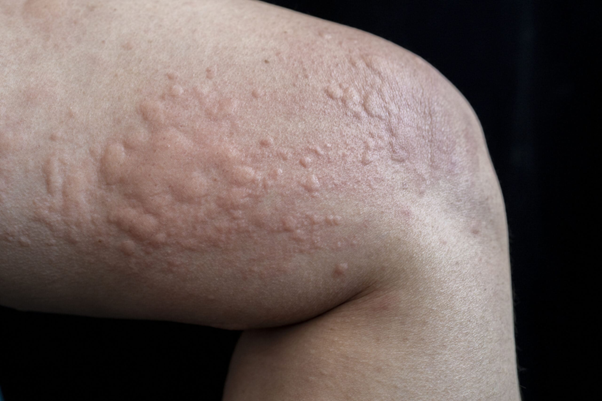
What are the Causes of Urticaria?
Urticaria can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Allergic reactions (food, medication, insect stings)
- Infections (viral, bacterial, or fungal)
- Physical stimuli (heat, cold, pressure, sunlight) – Physical urticaria
- Stress or emotional factors
- Autoimmune conditions
- Certain medications, such as antibiotics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
What are the symptoms of Urticaria?
- Red or skin-colored welts
- Intense itching
- Swelling (angioedema) around the lips, eyes, or other body parts
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Symptoms may worsen at night (due to falling body cortisol levels)
How is urticaria diagnosed?
A doctor may diagnose urticaria based on physical examination and medical history. In some cases, allergy tests, blood tests, or skin biopsies may be necessary to determine the underlying cause.
What are the treatment options for Urticaria ?
The treatment of urticaria depends on its cause and severity. Common approaches include:
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding allergens or irritants can prevent recurrence.
- Vit D levels corrected
- Treating an underlying (commonly ignored) chronic infection – Dental caries, worms in the intestine, sinusitis etc,.
- Antihistamines: Non-drowsy antihistamines like cetirizine or loratadine help control itching and swelling.
- Corticosteroids: In severe cases, short-term use of oral corticosteroids may be prescribed.
- Epinephrine: For severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), an epinephrine injection (EpiPen) may be required.
When to see a Doctor ?
- Symptoms significantly impact daily life
- Hives persist for more than a few days or recur frequently.
- You experience difficulty breathing, dizziness, or swelling of the throat (this may indicate anaphylaxis, which requires emergency care).
